Evaluation of an Automated Microscope Using Machine Learning for the Detection of Malaria in Travelers Returned to the UK
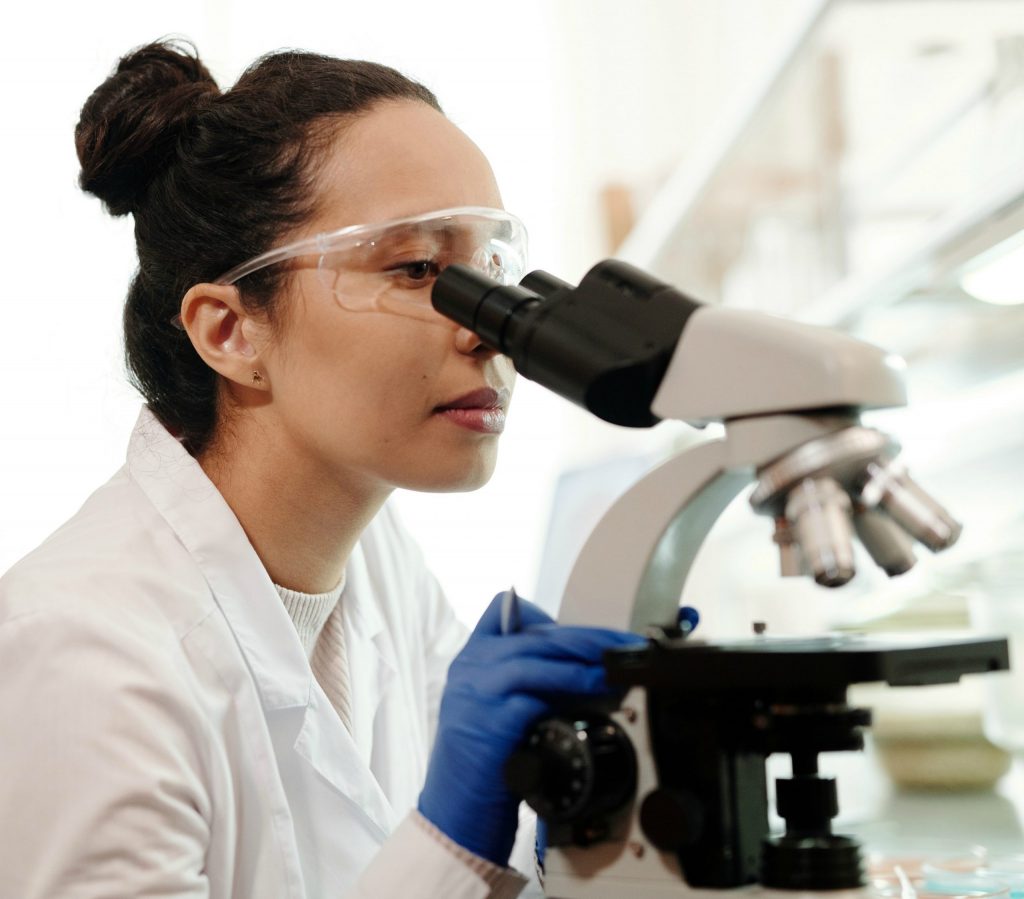

In this work, a team evaluated EasyScan GO to determine if it could detect, quantitate, and identify malaria parasites present in Giemsa-stained blood lms with consistency and accuracy compared to trained microscopists.
Multi-centric Field Evaluation Of A Digital Malaria Microscopy Device Based On Machine-Learning: EasyScan GO – A Preliminary Analysis
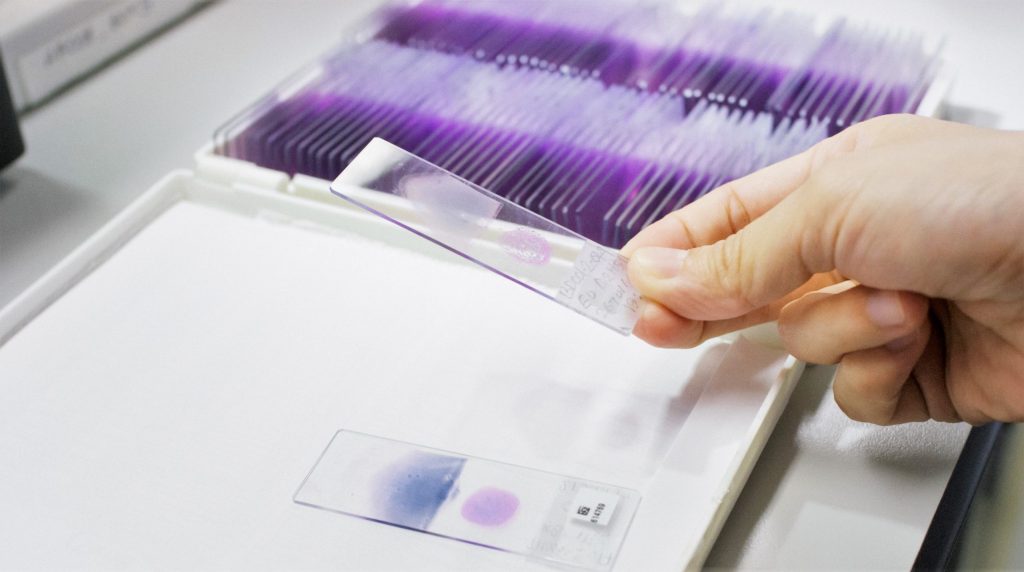

In this work, a team assessed the performance of the EasyScan Go, a microscopy device employing machine learning-based image analysis to detect malaria parasites.
Maintaining Focus with Remote Pathology Tools

We explain how a superior autofocus plays a crucial role in live remote consultations, especially for time-sensitive procedures, compared to autofocus in other systems.
Reviewing a Frozen Section with Motic’s FS-Live

During this tutorial, Dr. Enric Solans from Uchicago Ingalls Memorial Hospital, joins Motic Digital Pathology to explain how his lab has enabled real-time remote consultations using Motic’s FS-Live software.
International Telepathology
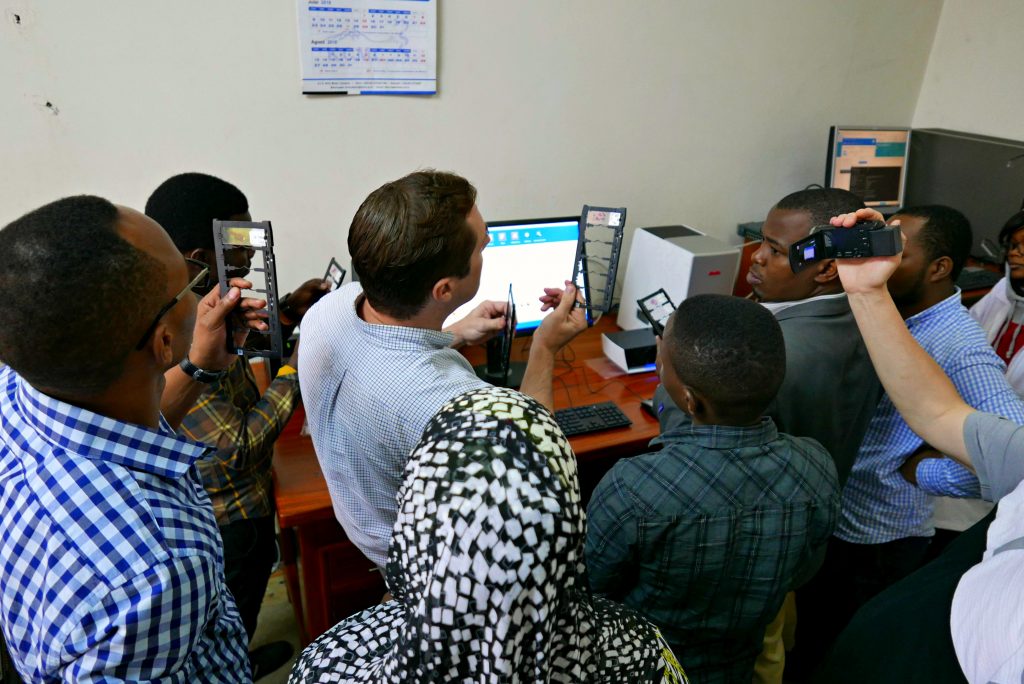

First featured at the ASCP Virtual 2020 conference, Drs. Cristina Costales (Stanford) and Enric Solans (UChicago Ingalls) demonstrate and discuss their experiences of using telepathology in working with remote international sites.
In VivA Deep Learning-Based System (Microscan) for the Identification of Pollen Development Stages and Its Application to Obtaining Doubled Haploid Lines in Eggplant
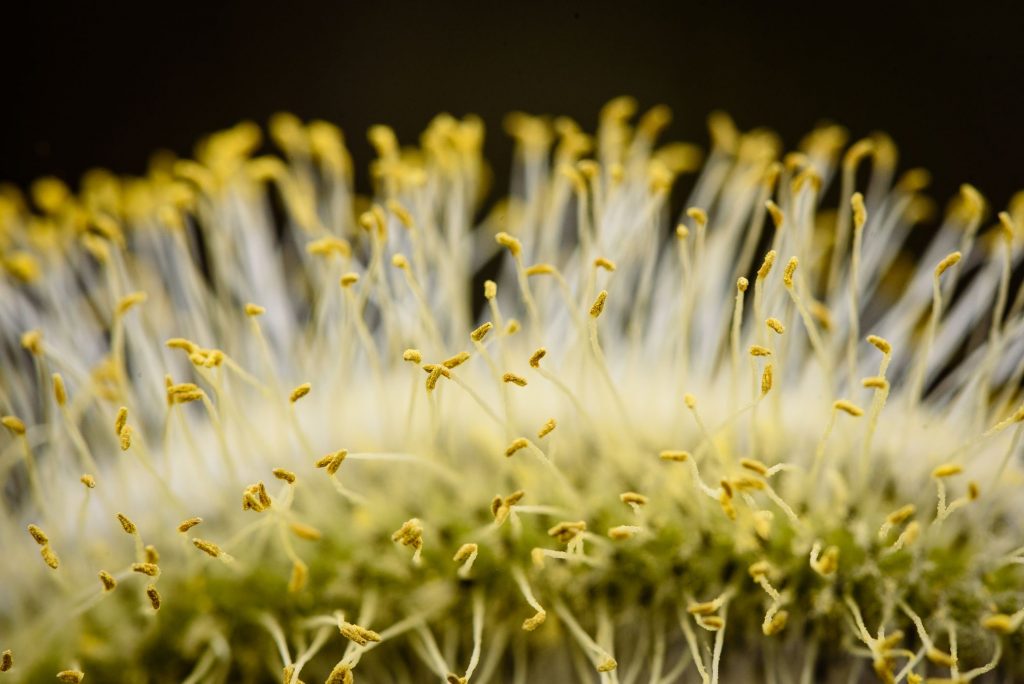

In this work, a team in Spain, developed Microscan, a deep learning-based system for the detection and recognition of the stages of pollen development. Check out the role of our MoticEasyScan in the study here.
In Vivo Remodeling of a 3D-Bioprinted Tissue Engineered Heart Valve Scaffold
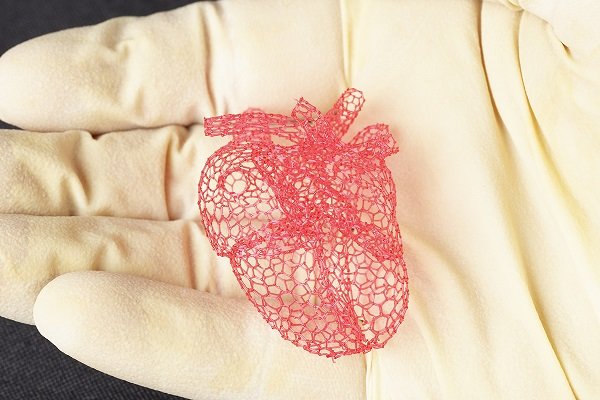

To evaluate the recellularization potential of a bioprinted aortic heart valve scaffold printed with highly concentrated Type I collagen hydrogel (Lifeink® 200) and MSCs. Check out the role our MoticEasyScan in this study here.
A Novel Transplantable Model of Lung Cancer-Associated Tissue Loss and Disrupted Muscle Regeneration
Cancer-associated muscle wasting (CAW), a symptom of cancer cachexia, is associated with approximately 20% of lung cancer deaths and remains poorly characterized on a mechanistic level. Read more about how MoticEasyScan contributed to this case study here.
Motic and the ASCP: Enabling Remote Diagnostics in Underserved Areas through Telepathology

International telepathology can help bridge the gap for cancer detection and diagnosis in less fortunate countries. In this post, MoticFlow users share perspectives and insights as to how the platform has made a difference for both the local hospitals and their patients as well as the consulting specialists.
Evaluation of the VETSCAN IMAGYST: an In-Clinic Canine and Feline Fecal Parasite Detection System Integrated with a Deep Learning Algorithm
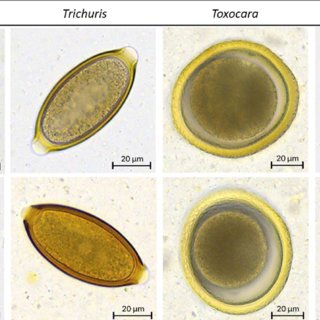
Fecal examination is an important component of routine companion animal wellness exams. Read more about how MoticEasyScan contributed to this case study here.


