Authors: Nathan Cleaver, DO, Byron Barksdale, DO, Amin Hedayat, DO, Kabeer Shah, DO, Mike Keeney, DO.
Introduction
Remote desktop solutions have become increasingly popular in recent years as more businesses and individuals adopt a flexible approach to work. These solutions allow users to remotely access their computers, applications, and data from anywhere in the world, making it easier to work remotely. Over the past 30 years, telepathology has become increasingly popular and real-time telepathology is a useful tool for remote diagnostics, consultation, and education. [1-8] Given the COVID-19 pandemic, physician shortages, and need to remote subspecialty expertise; remote work has become more prevalent within the pathology arena. [8] Notably, pathologist comparison of the available remote desktop software solutions has not previously been published. This study compares the technical and functional aspects of five popular remote desktop solutions for real-time telepathology while utilizing the Motic Digital Pathology suite.
Methods
Five board-certified pathologists/dermatopathologists located across the United States participated in this study. Motic USA provided the MoticEasyScan Pro 6 physically located in San Francisco, CA. The scanner requires an associated computer with a recorded internet connection speed. Motic Easy scanner software was utilized for the study and representative deidentified frozen section slides (N=3) were selected.
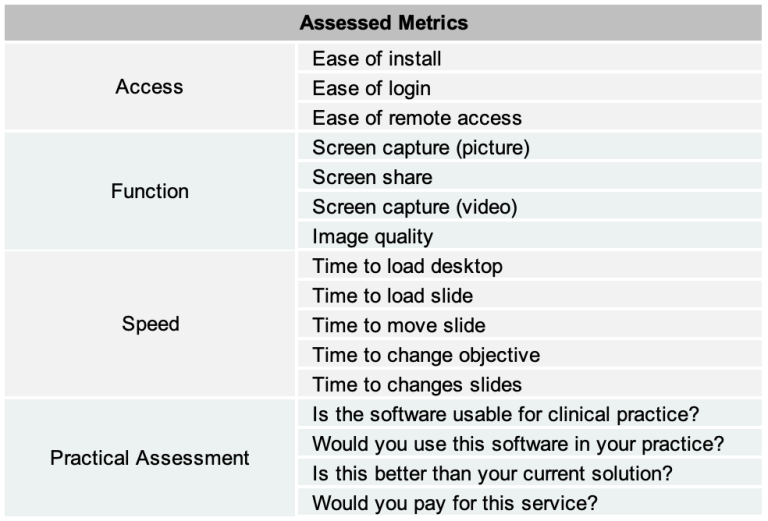
Table1: Assessed Metrics table. Five popular remote access software solutions were selected for comparison; AnyDesk, MS Teams, Parsec, Splashtop, and TeamViewer.
Two surveys (pre-survey and post-survey) were developed to capture the (1) technical aspects of the survey respondent’s remote computer and internet connection and (2) functionality and opinion regarding the software experiences. Each of the respondents were provided education on the installation, access, and functionality of the Motic EasyScan software and remote access software solutions. Then each respondent was instructed to complete a series of tasks (manipulate each of the three frozen section slides and attempt a snapshot/screen share, and screen record) to mimic practical use of a remote access platform. Opinions regarding each of the five software were recorded across three major metrics, (1) ease of access, (2) functionality, (3) perceived speed. Each software was ranked (1-Best; 5-Worst) across each survey question (Table 2). In addition, a practical appraisal comparing the software solutions was performed based on clinical use, comparison to current methods, and fees (published as of study date). [9-13]
Respondent technical pre–survey results were summarized, and post-survey results summed, and comparative average ranks given for each survey category. As for the practical appraisal, “Yes” responses were rank summed. Finally, comments were collated for each subsection.
Results
Each of the respondents (N=5) completed the pre-survey and post-surveys including the practical appraisal.
Pre-survey
80% (N=4) pathologists utilized Apple iOS while 20% utilized a PC. 60% utilized a laptop with N=2 using the standard 15’ display. Others utilized 27” and 61” monitor displays. The range of processor speeds includes 2.3GHz i9 – 3.6Ghz i5. The majority of respondents (N=4) used 16GB RAM with built in Intel HD graphics cards (1536MB). 60% (N=3) utilized a mouse, while 40% utilized a track pad. All users utilized WiFi with download speeds ranging 246.90 – 453.65 Mbps (average 382.52 Mbps) and upload speeds ranging 23.2-263.47 Mbps (average 143.3 Mbps).
Two respondents utilize real time telepathology services for clinical practice, two for educational purposes, and three do not currently utilize real-time telepathology. Of the telepathology users, one uses MS teams and the other Zoom. Only one currently enjoys the functionality of the used telepathology platform.
Post-survey
Results are summed and tabulated in Table 2. In terms of access, AnyDesk and MS Teams ranked top two with Parsec the lowest. Comments confirm that simplistic design, unattended access and dual factor authentication was preferred. TeamViewer ranked highest in functionality with Parsec the lowest with comments including preference for design simplicity (single button rather than task panes) and desire for file saving to local computer rather than remote computer.
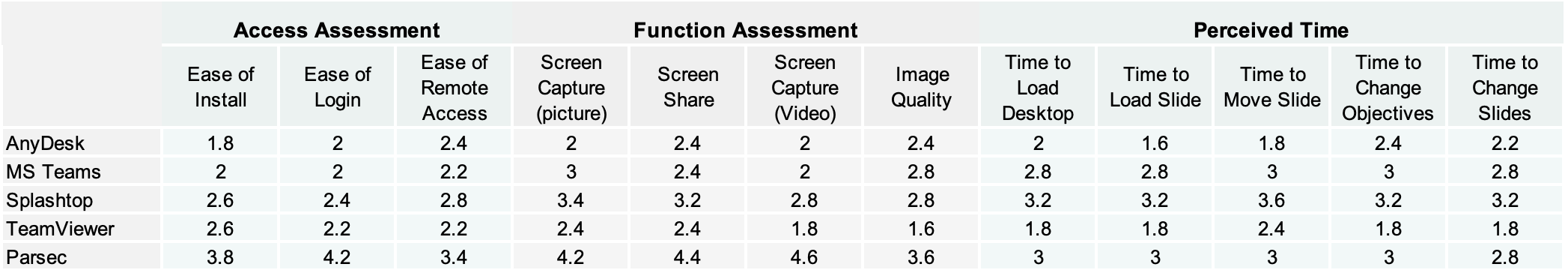
Table 2: Average Assessment Data
TeamViewer was perceived as the fastest with AnyDesk a close second and Splashtop and Parsec the slowest. Comments note that MS Teams and Splashtop also showed significant latency and AnyDesk required longer latency to rasterize the image compared to TeamViewer. Importantly, most reviewers noted image quality across all platforms was similar. Overall, respondents ranked TeamViewer as superior with AnyDesk a close second. Parsec was the lowest overall rank. Table 3 shows a summary of best solutions per assessed metric.
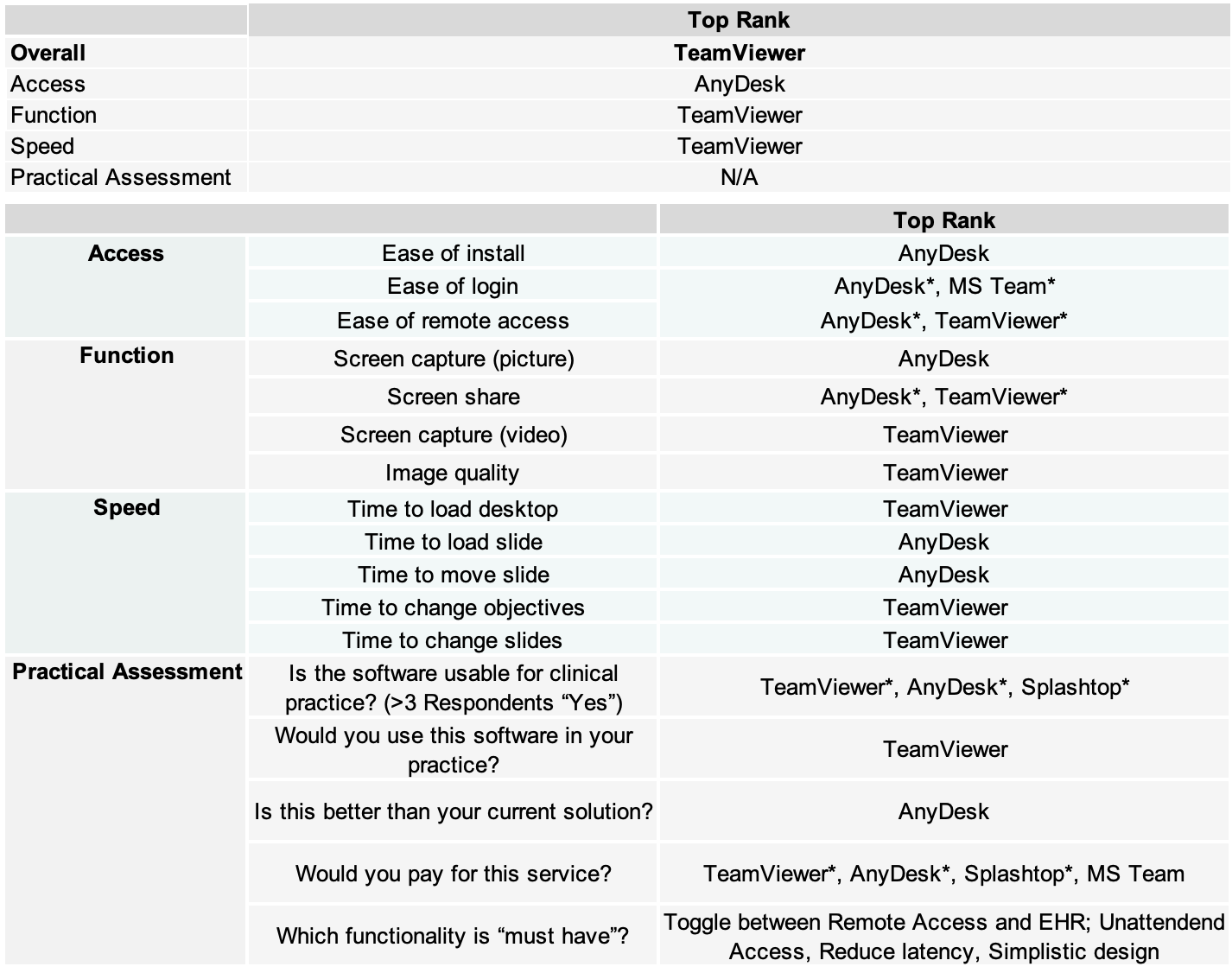
Table 3: Summary of Best Remote Desktop Solutions
*Tied rank
Discussion
In terms of remote real-time telepathology software, TeamViewer was recognized as the overall best platform in terms of access, functionality, and speed. In addition, a majority of respondents would recognize the software as capable for clinical practice (rapid on-site assessment, Mohs, frozen section). Notable functionality which improved usability included simplistic design, unattended access, and reduced latency. Real time telepathology workflows are most utilized for limited resource settings, such as remote hospitals or even successfully deployed in international locations. [3,4] Though international connections were not tested in this study, the user experiences gleaned are portable globally.
In terms of access, AnyDesk, MSTeams, and TeamViewer were recognized as high performers. Each tested software was compatible with iOS and Windows platforms. Functionality not tested here, but of the utmost importance includes security. AnyDesk uses end-to-end encryption to ensure that all data transmitted between devices is secure. [10] Microsoft Teams uses industry-standard security protocols such as TLS and SRTP to secure data in transit and at rest. [11] Parsec also uses encryption to secure its remote desktop connections. [13] Splashtop uses AES-256 encryption to secure its connections [12], while TeamViewer uses 256-bit RSA key exchange and AES-256 session encryption. [9] A functional assessment by local-regional information technology security should be performed prior to implementation to remain HIPAA compliant.
Functionality assessment demonstrated AnyDesk and TeamViewer as superior. This is largely due to the simplicity of design and button configuration. Notably, not all users would utilize the functionality tested (screen capture or screen share), however, this simple test allowed for a deeper assessment of the menu and functionality of the software should it be required. Within clinical settings, a second remote consultation may be necessary and screen sharing would be useful for second opinion or subspecialty-based consultation. [1-4,6,8] Video recording or screen capture can be used for educational purposes such as lectures, rounds, tumor boards. [7] Each remote desktop solution offers unique features that set it apart from the others. AnyDesk offers features such as file transfer, session recording, and remote printing. Microsoft Teams offers features such as screen sharing, chat, and video conferencing. Parsec is designed specifically for gaming and offers features such as low-latency streaming and gamepad support. Splashtop offers features such as remote wake, multi-monitor support, and session recording. TeamViewer offers features such as file transfer, remote printing, and multi-platform support. These features may not be relevant for specific clinical settings, however, each institution should carefully compare available functionality. Image quality was not a comparative difference for most respondents and was not a critical factor of this study, however, was included should there be significant difference between platforms. Previous publications have shown telepathology, once validated, is a robust clinical system for clinical practice.[1-4]
Speed perception results showed TeamViewer to be superior, however, AnyDesk was a noted close second. Several comments, demonstrated rasterization times to be slower with AnyDesk comparative to TeamViewer. AnyDesk uses a proprietary video codec called DeskRT to provide a smooth and responsive remote desktop experience. [10] While TeamViewer uses high-speed data channels and optimized image processing to provide fast and responsive performance. [9] This software difference may have led to varied experiences. Splashtop and Parsec were notably “slowest” though Parsec uses its own low-latency streaming technology to provide “high-quality graphics and minimal lag”. [13] Splashtop claims to provide “up to 10x faster performance” than other remote desktop solutions, though its methodology is unclear. [12] Microsoft Teams uses adaptive bandwidth technology to optimize performance based on network conditions which may have led to variable experiences. [11]
Within the practical assessment, an attempt to realize the actual value of the remote system was made. A comparison of currently utilized software and value within one’s own practice was made. Notably, two respondents currently utilized real-time telepathology with only one of them satisfied with the current software (MS Teams). Though that pathologist remained confident in that software (MS Teams) at the conclusion of the study, 80% of pathologists noted TeamViewer as preferred in their practice. In addition, AnyDesk was noted by two pathologists to be superior to their current software and one noted Splashtop and TeamViewer to be superior as well. When presented with pricing for each remote software, pathologists were amenable to 4 of the 5 solutions. Of note, one pathologist noted current latency relative to expense to be impractical for their current use and another suggested MS Teams as an acceptable compromise given the bundle with the MS Suite. Prior studies have suggested price as a barrier to utilization for telepathology [5], however Laurent-Bellue et al, demonstrated a similar annual expense when comparing a real time pathology implementation to pathologist time and courier costs. [6]
Notable limitations of the study include a low number of survey respondents with individual opinions and perceptions of speed, ease, and remote internet connections. In addition, hospital-based security and firewalls were not tested in this study which may change user experiences.
Conclusion
In this study, TeamViewer provided the overall best experience for pathologists and dermatopathologists in terms of access, functionality, and speed. However, AnyDesk, MS Teams, and Splashtop were noted to be acceptable and equal, if not better to current solutions.
In conclusion, choosing the right remote desktop solution depends on users’ specific needs and preferences and should be tested in the clinical environment with which it will be deployed.
Reference:
References:
- Rohr JM, Ginnebaugh K, Tuthill M, Pimentel J, Markin R. Real-time Telepathology Is Substantially Equivalent to In-Person Intraoperative Frozen Section Diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2023 Mar 15.
- Carll T, Siddiqui F, Agni M, Poon R, Nash C, Gettings C, Cipriani N. Validation and implementation of Aperio LV1 remote live view telepathology system for intraoperative frozen section diagnosis. J Pathol Inform. 2023 Feb 3.
- Kothari K, Damoi JO, Zeizafoun N, Asiimwe P, Glerum K, Bakaleke M, Giibwa A, Umphlett M, Marin M, Zhang LP. Increasing access to pathology services in low- and middle-income countries through innovative use of telepathology. Surg Endosc. 2023 Sep;37(9):7206-7211.
- Pinto DG, Bychkov A, Tsuyama N, Fukuoka J, Eloy C. Real-World Implementation of Digital Pathology: Results from an Intercontinental Survey. Lab Invest. 2023.
- Giambrone D, Rao BK, Esfahani A, Rao S. Obstacles hindering the mainstream practice of teledermatopathology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Oct;71(4):772-80.
- Laurent-Bellue A, Poullier E, Pomerol JF, Adnet E, Redon MJ, Posseme K, Trassard O, Cherqui D, Zarca K, Guettier C. Four-Year Experience of Digital Slide Telepathology for Intraoperative Frozen Section Consultations in a Two-Site French Academic Department of Pathology. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 Aug 5;154(3):414-423.
- Rani, R. Vatchala, et al. “Virtual microscopy: The future of pathological diagnostics, dental education, and telepathology.” Indian Journal of Dental Sciences 13.4 (2021): 283-283.
- Petersen JM, Jhala N, Jhala DN. The Critical Value of Telepathology in the COVID-19 Era. Fed Pract. 2023 Jun;40(6):186-193.
- TeamViewer, 20 Oct. 2023, www.teamviewer.com/en-us/.
- AnyDesk, anydesk.com/en. Accessed 2 Nov. 2023.
- Video Conferencing, Meetings, Calling | Microsoft Teams, www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-teams/group-chat-software. Accessed 2 Nov. 2023.
- Splashtop, www.splashtop.com/. Accessed 2 Nov. 2023.
- Parsec, app/. Accessed 2 Nov. 2023.